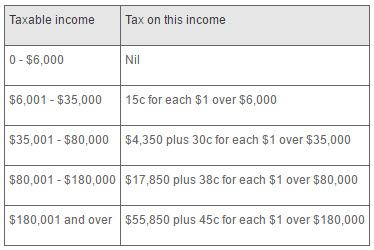
Situation:
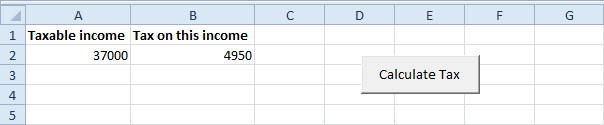
1. First, we declare two double variables. One double variable we call income, and one double variable we call tax.
Dim income As Double2. We initialize the variable income with the value of cell A2 and round it.
Dim tax As Double
income = Round(Range("A2").Value)3. We place the rounded value into cell A2 again.
Range("A2").Value = income4. We use the Select Case statement to calculate the tax on an income. Excel VBA uses income to test each subsequent Case statement to see if the code under the Case statement should be executed.
Select Case incomeExample: if income is 37000, tax equals 4350 + 0.3 * (37000-35000) = 4350 + 600 = $4950
Case Is >= 180001
tax = 55850 + 0.45 * (income - 180000)
Case Is >= 80001
tax = 17850 + 0.38 * (income - 80000)
Case Is >= 35001
tax = 4350 + 0.3 * (income - 35000)
Case Is >= 6001
tax = 0.15 * (income - 6000)
Case Else
tax = 0
End Select
5. We write the value of the variable tax to cell B2.
Range("B2").Value = tax6. Place this code in a command button and test it.
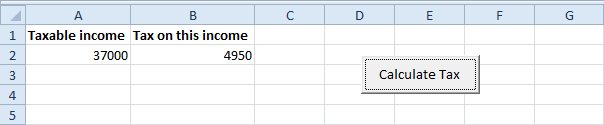
Result:
 .
.

