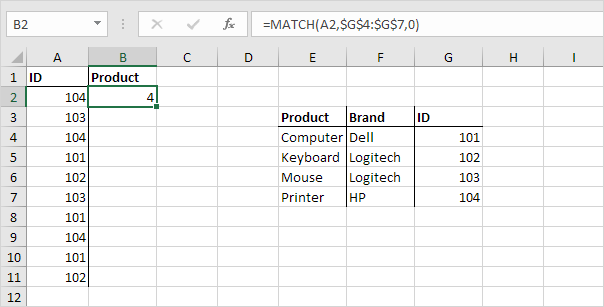
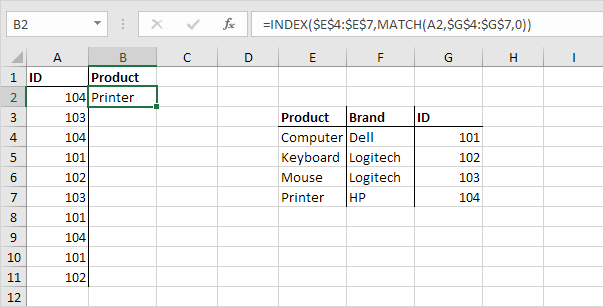
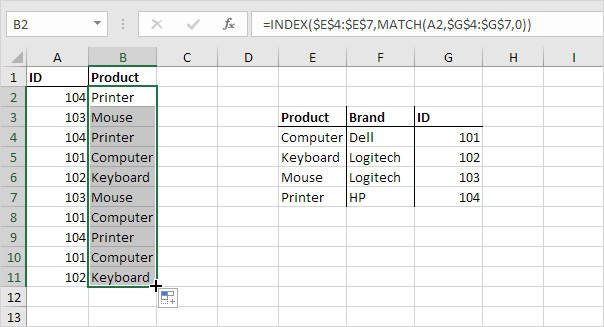
The INDIRECT function in Excel returns the reference specified by a text string.
1. For example, the INDIRECT function below reduces to =INDIRECT("C2"), =C2, 5

Do we really need the INDIRECT function for this? Yes. Below you can find the result without using the INDIRECT function.

2. For example, the function below reduces to =SUM(INDIRECT("E3:E6")), =SUM(E3:E6), 27

Note: the & operator is used to join strings. Border for illustration only.
3. For example, the function below reduces to =AVERAGE(Scores), 9

Note: the named range Scores refers to the range C2:C4..
Read More »
1. For example, the INDIRECT function below reduces to =INDIRECT("C2"), =C2, 5

Do we really need the INDIRECT function for this? Yes. Below you can find the result without using the INDIRECT function.

2. For example, the function below reduces to =SUM(INDIRECT("E3:E6")), =SUM(E3:E6), 27

Note: the & operator is used to join strings. Border for illustration only.
3. For example, the function below reduces to =AVERAGE(Scores), 9

Note: the named range Scores refers to the range C2:C4..








 .
.