Next Page: This option inserts a section break and moves text after the break to the next page of the document.
Continuous: This option inserts a section break and allows you to continue working on the same page.
Even Page and Odd Page: These options add a section break and move the text after the break to the next even or odd page. These options may be useful when you need to begin a new section on an even or odd page (for example, a new chapter of a book).
types of section breaks
To insert a section break:
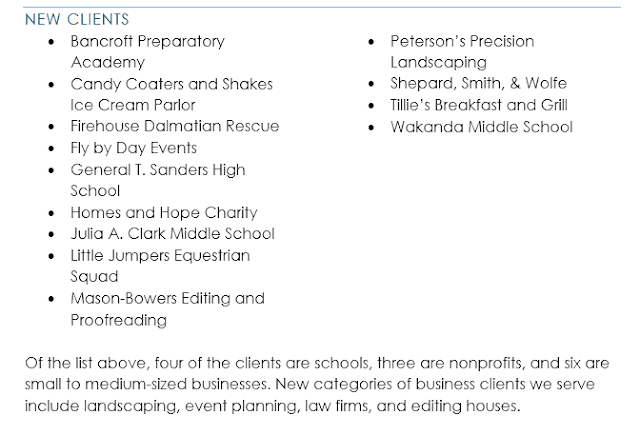
In our example, we'll add a section break to separate a paragraph from a two-column list.
Place the insertion point where you want to create the break. In our example, we'll place it at the beginning of the paragraph we want to separate from two-column formatting.
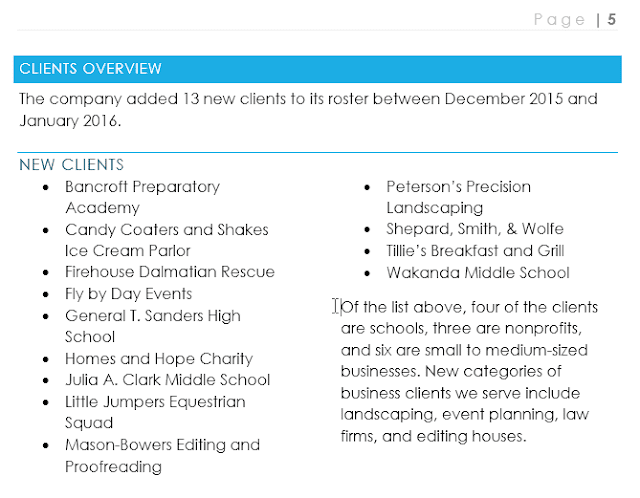
On the Page Layout tab, click the Breaks command, then select the desired section break from the drop-down menu. In our example, we'll select Continuous so our paragraph remains on the same page as the columns.
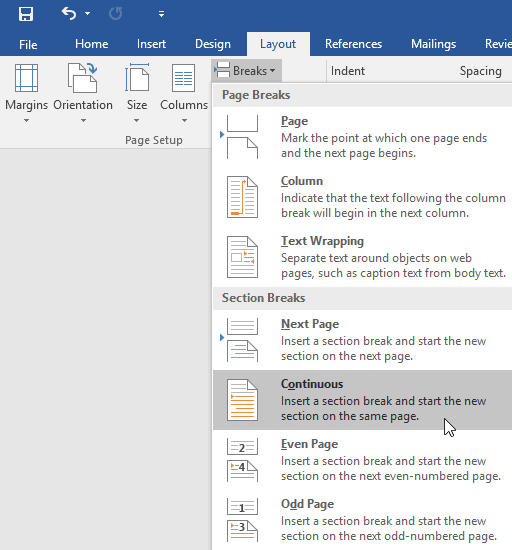
A section break will appear in the document.
The text before and after the section break can now be formatted separately. In our example, we'll apply one-column formatting to the paragraph.
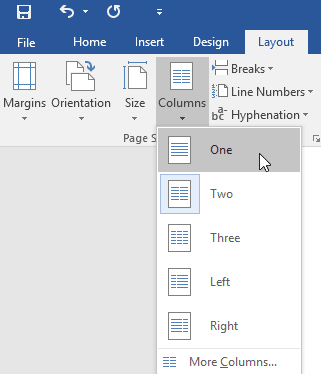
The formatting will be applied to the current section of the document. In our example, the text above the section break uses two-column formatting, while the paragraph below the break uses one-column formatting.
 .
.
